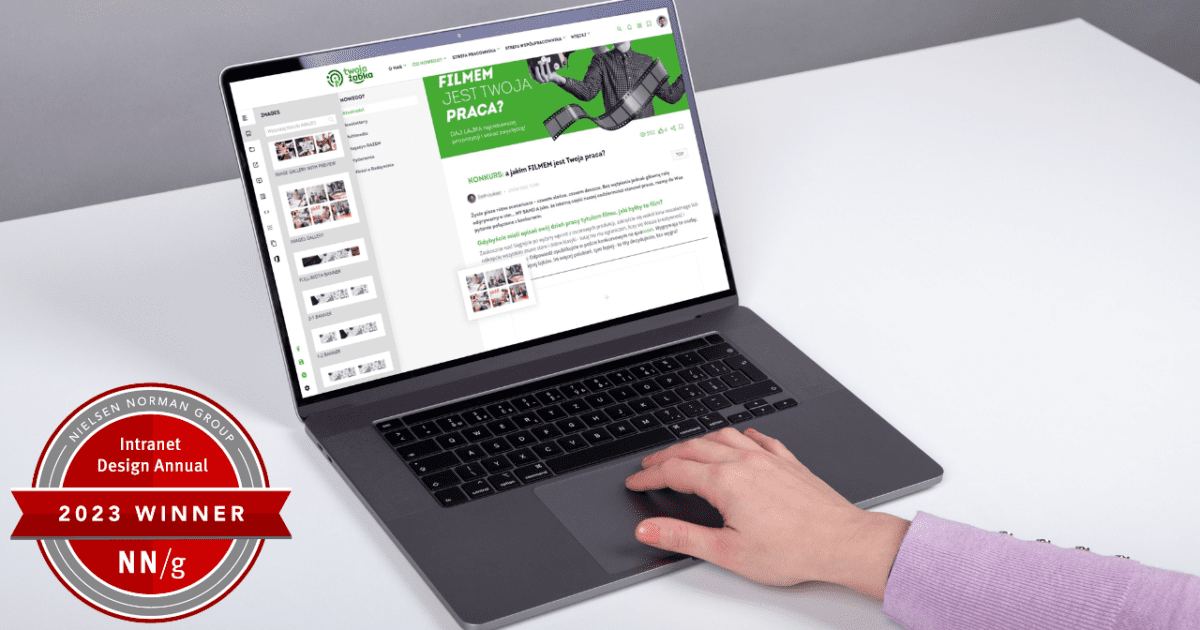

5 key challenges in creating an intranet
Whether you’re on the intranet stakeholder team or part of the team implementing it, success is the goal. However, creating an intranet comes with challenges. This article dives into the top 5 hurdles, from tech issues to user adoption, revealing the complexities involved. Overcoming these obstacles unlocks the intranet’s potential for a connected, collaborative workspace. Trust our experience (proven by three NN/g awards!) for successful implementation and dive into fixes.
5 key challenges in creating an intranet
Challenge 1: Designing a user-friendly interface

Creating an intranet with an intuitive and user-friendly interface that takes into account the diverse needs and preferences of users is a complex undertaking. The challenge involves various complex aspects that require careful consideration and meticulous planning. A key aspect of this challenge is designing a new information architecture (IA) that improves user experience (UX), enhances search capabilities, and simplifies content discovery.
💡 The Fix
In response to the challenges of designing a user-friendly interface, a strategic approach that prioritizes user experience (UX) design is becoming paramount. This approach includes several key steps when creating an intranet designed to ensure that the interface effectively meets user needs and preferences while mitigating potential complexities.
- Prioritize User Experience (UX) Design: At the heart of addressing the challenge lies a strong emphasis on user experience design. This involves crafting an interface that aligns with users’ mental models, expectations, and behaviors. By placing users at the center of the design process, the resulting interface becomes more intuitive and user-friendly. To ensure smooth and fast content creation, choose a solution with an easy-to-use drag-and-drop CMS.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Usability testing serves as a crucial method for evaluating the interface’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios. By observing how actual users interact with the interface, designers can identify pain points, areas of confusion, and opportunities for improvement. Regular usability testing sessions provide valuable insights that inform iterative refinements. Any analytics modules or heatmaps will be helpful for you.
- Gather Input from Diverse User Groups: User preferences and needs can vary widely across different user groups within the organization. Engaging with a diverse range of users, from various departments and roles, helps in obtaining a comprehensive understanding of their unique requirements. This input informs design decisions that cater to the broadest possible audience.
- Iterate on the Interface Based on Feedback: Continuous iteration is the cornerstone of successful interface design. Feedback gathered from usability testing and user feedback is used to iteratively improve the interface. This iterative process ensures that the design evolves according to user needs, solving problems and improving usability over time. When creating an intranet, remember that you should be able to collect user feedback on an ongoing basis, so multiple feedback channels should be provided.
Challenge 2: Content management complexity
Creating an intranet comes with the challenge of content management complexity, which can hinder the smooth operation and effectiveness of the platform. Managing different types of content, updates, and permissions can lead to confusion and clutter, potentially resulting in the proliferation of outdated or inaccurate information. The struggle to maintain up-to-date, high-quality content is further exacerbated by the risk of frustrating users and reducing trust in the reliability of the intranet. Solving this problem requires not only sophisticated tools but also a comprehensive strategy for content management, collaboration, and consistent quality assurance.
💡 The Fix
Organizations creating an intranet can implement the following measures to mitigate these challenges:
- Clear Content Categorization System: Establishing a well-defined content categorization system is paramount. This ensures that content is organized logically, making it easier for users to locate information. Categories could be based on topics, departments, or any relevant classification that aligns with users’ needs.
- Roles for Content Ownership: Assigning clear roles and responsibilities for content ownership is essential. This prevents content from becoming scattered and unaccounted for. Designating individuals or teams as content owners encourages timely updates and accountability.
- User-Friendly Content Management Tools: Employ content management tools with intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. This ensures that editors, even those with minimal training, can efficiently create and manage content. Features such as drag-and-drop functionality and dedicated content types simplify the content creation process.
- Establish a Review Process: Implement a structured review process where content created by local editors is reviewed by global editors before publication. This helps maintain editorial standards, accuracy, and consistency across the intranet. A unified publication workflow will make the process smooth and clear.
- Regular Content Audits: Conduct regular content audits to ensure that the information presented remains accurate and up to date. Outdated or irrelevant content should be identified and either updated or removed. Settle on a solution in which the system itself asks you if the content is up to date.
Challenge 3: Information overload
Another major challenge when creating an intranet is a phenomenon known as “information overload.” This phenomenon occurs when an intranet becomes flooded with excessive amounts of information, causing users to feel overwhelmed and making it difficult for them to locate relevant content.

The consequences of information overload are multifaceted, ranging from reduced productivity to frustration among users, ultimately limiting the intranet’s effectiveness as a communication and collaboration tool.
The challenge of information overload arises from the intrinsic desire to provide comprehensive resources to users, often resulting in an accumulation of content that surpasses users’ capacity to digest and navigate effectively. This is exacerbated by the diverse nature of content types ranging from documents and news articles to images and videos each vying for attention within the same platform.
💡 The Fix
To overcome this challenge, organizations creating an intranet should adopt strategies that prioritize relevance, accessibility, and content curation:
- Content Curation: Implement a content curation strategy that involves the careful selection and organization of information. This ensures that only the most relevant and valuable content is prominently featured, reducing clutter and enhancing user experience.
- Search and Navigation: Develop robust search and navigation features that allow users to quickly locate specific content. Incorporating filters, tags, and intuitive search functionalities can significantly ease the process of content discovery.
- Personalization: Implement personalization features that tailor content recommendations based on users’ roles, preferences, and past interactions. This ensures that users are presented with content that aligns with their specific needs.
- Content Prioritization: Clearly prioritize and categorize content, distinguishing between essential information and supplementary resources. This helps users quickly identify critical updates or resources amidst the plethora of available content.
- User Training: Offer user training sessions to teach employees how to effectively navigate the intranet, utilize search features, and filter content. Empowering users with the skills to efficiently find information can alleviate the challenges posed by information overload.
- Regular Content Review: Regularly review and update content to ensure its accuracy and relevance. Remove outdated or redundant information to prevent content bloat.
Challenge 4: Technical integration and compatibility
The challenge of “Technical integration and compatibility” is a critical consideration when creating an intranet. This challenge revolves around the intricate task of seamlessly integrating the intranet with existing systems and guaranteeing its compatibility across a diverse array of devices and platforms.

💡 The Fix
To overcome the challenges associated with technical integration and compatibility, organizations can employ the following strategies, drawing from the provided information:
- Select an Intranet Platform with Robust Integration Capabilities: The choice of an intranet platform plays a pivotal role in addressing integration challenges. Opt for an intranet solution that boasts robust integration capabilities, including the ability to seamlessly connect with existing systems and applications. This ensures that data can flow efficiently between the intranet and other tools.
- Collaborate Closely with IT Teams: Collaboration between intranet project teams and IT teams is essential for ensuring smooth integration. IT teams possess the technical expertise necessary to navigate complex integration processes. Collaborate closely with IT experts to plan, execute, and troubleshoot integration tasks effectively.
- Combine Multiple Tools into One Coherent Platform: In cases where the intranet needs to serve as a central hub for various functions, such as knowledge sharing, social networking, e-learning, and resource reservation, conduct extensive meetings at both technical and business levels. These meetings are essential to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the diverse use cases the intranet must support. Engage with managers and end-users to gather insights into their specific needs and expectations.
- Leverage Ready-to-Go Products with Custom Integrations: Consider adopting ready-to-go products like Workai that come equipped with many pre-built features and scenarios. This minimizes the need for extensive custom development and initial analysis for core functionalities. Such products allow organizations to focus on custom integrations and additional features that cater to their unique requirements.
- Iterative Approach to Development: Adopt an iterative approach to intranet development. Begin by addressing the most critical functionalities and customizations based on stakeholder requests. Follow a structured process encompassing concept-building, mock-ups, development, and user testing for each new feature or customization. This iterative approach ensures that the intranet evolves in line with evolving needs and user feedback.
By incorporating these strategies, organizations can effectively tackle the technical integration and compatibility challenges associated with creating an intranet. The result is a well-integrated, user-friendly, and feature-rich intranet that serves as a central hub for communication and collaboration across the organization.
Challenge 5: User adoption and engagement
Another major challenge when creating an intranet is achieving user acceptance and engagement. Encouraging employees to actively use and interact with an intranet can be a difficult task. This challenge stems from the fact that if users do not see value in the intranet or find it cumbersome to navigate, adoption rates tend to be disappointingly low.
User adoption and engagement are critical to the success of an intranet, as they directly affect its effectiveness as a platform for communication and collaboration.
💡 The fix
To overcome the challenge of user adoption and engagement in the context of creating an intranet, organizations can employ a multifaceted approach that incorporates the following strategies, drawing from the provided information:
- Create an Intuitive and User-Friendly Interface: Start by designing the intranet with a focus on user experience (UX). An intuitive and user-friendly interface is paramount in encouraging user engagement. Ensure that navigation is straightforward, and information is logically organized to reduce friction in accessing content.
- Conduct User Testing: Regularly conduct user testing to identify pain points and areas of confusion within the intranet. Engage real users to provide feedback on their experiences. This process helps in pinpointing usability issues and informs iterative improvements to enhance the intranet’s overall user-friendliness.
- Regularly Update and Personalize Content: Keep content fresh and relevant by regularly updating it. Outdated or stale information can deter users from engaging with the intranet. Additionally, implement personalization features that allow users to tailor their content preferences, ensuring they receive information that is most pertinent to their roles and interests.
- Analytics: Leverage analytics to gain insights into user behavior and engagement patterns. Analyze data to understand which sections of content are most popular and which may require improvement. Data-driven decisions can guide enhancements that resonate with users.
- Feedback Channels: Establish accessible and user-friendly feedback channels where users can provide input, report issues, and share suggestions. Actively listen to user feedback and use it to make informed enhancements. Transparency in addressing user concerns fosters trust and engagement.
- Ready-to-Use Content Templates: Utilize pre-designed content templates that are ready to use. These templates simplify the content creation process, ensuring consistency and saving time for content editors. Users are more likely to engage with well-structured and visually appealing content.
- Multiple Communication Channels: Utilize a variety of communication channels to engage different audiences. Beyond the intranet itself, leverage social media, Microsoft Teams, newsletters, and mobile applications to disseminate information and encourage participation. These channels reach users where they are most comfortable and active.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can create an environment that not only addresses the challenge of user adoption and engagement but also fosters a thriving intranet ecosystem. An intuitive interface, regular content updates, personalization, feedback-driven improvements, and diverse communication channels collectively contribute to a user-centric and engaging intranet experience.
Conclusion
In today’s ever-evolving business landscape, where connectivity and information exchange are paramount, the role of intranets in fostering effective communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing within organizations cannot be overstated. However, as we’ve explored in this article, the journey to creating a truly successful intranet is laden with its share of challenges.
From the complexities of designing a user-friendly interface to managing the intricate web of content and battling the overwhelming information overload, organizations must navigate these obstacles strategically. Moreover, seamless technical integration and compatibility are key to ensuring that the intranet functions seamlessly across diverse devices and platforms.
Workai is a powerful ally in overcoming the challenges of creating an intranet. Its user-friendly interface, content management capabilities, content selection tools, integration flexibility, and user engagement features collectively contribute to the success of intranet projects, helping organizations create thriving and effective intranet ecosystems. Elevate your intranet project with our award-winning implementation process, designed by Workai experts to conquer challenges and achieve your goals from day one.
